HTD
[Python] 백준 1799번: 비숍 본문
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1799
1799번: 비숍
첫째 줄에 체스판의 크기가 주어진다. 체스판의 크기는 10이하의 자연수이다. 둘째 줄부터 아래의 예와 같이 체스판의 각 칸에 비숍을 놓을 수 있는지 없는지에 대한 정보가 체스판 한 줄 단위로
www.acmicpc.net
import sys
input = sys.stdin.readline
def dfs(puttables, index, count):
# Base case
if index == len(puttables):
global max_count
max_count = max(max_count, count)
return
# Recursive case
x, y = puttables[index]
nx, ny = new_positions[x][y]
if is_x_using[nx] == False and is_y_using[ny] == False:
is_x_using[nx] = True
is_y_using[ny] = True
dfs(puttables, index+1, count+1)
is_x_using[nx] = False
is_y_using[ny] = False
dfs(puttables, index+1, count)
if __name__ == '__main__':
N = int(input())
board = [list(map(int, input().split())) for _ in range(N)]
# Set new_positions
new_positions = [[[-1, -1] for _ in range(N)] for _ in range(N)]
for i in range(N):
new_positions[i][0] = [i, N-i-1]
for j in range(1, N):
new_positions[i][j][0] = new_positions[i][j-1][0] + 1
new_positions[i][j][1] = new_positions[i][j-1][1] + 1
# Set is_using
is_x_using = [False]*(N*2-1)
is_y_using = [False]*(N*2-1)
# Set puttables
puttables1 = []
puttables2 = []
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N):
if board[i][j] == 1:
if (i+j) % 2 == 0:
puttables1.append((i, j))
else:
puttables2.append((i, j))
# Set total_count
total_count = 0
max_count = 0
dfs(puttables1, 0, 0)
total_count += max_count
max_count = 0
dfs(puttables2, 0, 0)
total_count += max_count
# Print the result
print(total_count)
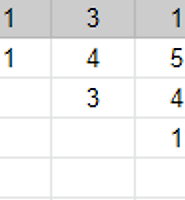
나는 이 문제를 풀기 위해 새로운 좌표를 도입하였다. 예제 입력 1(크기가 5일 때)에서는 아래와 같은 좌표가 도출된다.
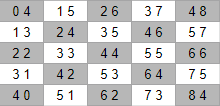
이를 통해 무엇을 할 수 있는지를 알면 아마도 감이 올 것이라고 생각한다. 위에서 2, 4에 해당하는 위치(좌표상으로는 1, 1)에 비숍을 놓았다고 하면, 비숍을 놓을 수 없는 곳은 아래와 같이 묘사된다.

특징을 보자. x가 2인 곳들을 모두 못 쓰게 되었으며, y가 4인 곳들도 모두 비숍을 둘 수 없게 되었다!
이 새로운 좌표(new_positions)에서 is_x_using, is_y_using이라는 리스트가 파생된다. 말그대로 해당 라인을 쓸 수 있는지를 저장하는 리스트이다.
(1, 1) 좌표에 비숍을 두어야 하는 상황을 가정해보자. is_x_using과 is_y_using를 수정해야하는데 이를 위해서는 (1, 1) 좌표에 해당하는 new_positions가 필요하다. 이것은 new_positions[1][1]을 통해 바로 얻을 수 있다. 이제 is_x_using[dx], is_y_using[dy]에 True를 넣어주기만 하면 된다!
이것을 기반으로 DFS 함수를 짜면 된다. 하지만 별다른 장치 없이 무작정 탐색을 하게 되면, N이 10이고 모두 1로 채워져있을 때 2^100번이라는 탐색을 감당해야한다.
이를 위해서는 또다른 특징 하나를 알아야만 한다.

위 사진에서 체크보드처럼 색을 입힌 이유가 있다. 검은색 칸과 흰색 칸은 서로 영향을 받지 않는다. 위에서 (1, 1)에 비숍을 두었을 때를 생각해보자. 그 어떤 흰색 칸에 영향을 미치지 않았다. 따라서 탐색을 총 2번 나누어 할 수 있다. 이렇게 되면, 기존의 시간복잡도인 O(2^N*N)에서 N이 N/2로 줄어든 것이므로 O(2^((N^2)/4))가 되어 이 문제를 풀 수 있다.
먼저 puttables라는 리스트를 2개를 두고, 여기에 board 값이 1인 좌표들을 저장한다. 다음으로 DFS를 2번 진행해주면 된다.
DFS는 단순하다. 만약 현재 좌표에 비숍을 둘 수 있다면 비숍을 두거나, 두지 않는 경우에 대해 탐색을 2번 해주고, 반대로 둘 수 없다면 당연지 두지 않는 탐색을 진행한다. 이것을 puttables1, puttables2에 대해서 진행해주면 된다.
'Algorithm > 백준' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Python] 백준 2162번: 선분 그룹 (0) | 2021.09.10 |
|---|---|
| [Python] 백준 2143번: 두 배열의 합 (0) | 2021.09.09 |
| [Python] 백준 11585번: 속타는 저녁 메뉴 (0) | 2021.09.07 |
| [Python] 백준 9202번: Boggle (0) | 2021.09.06 |
| [Python] 백준 1766번: 문제집 (0) | 2021.09.05 |